Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

Act as a barrier to most water-soluble substances the non-polar fatty acid tails prevent polar molecules or ions from passing across the membrane.
Cell membrane structure and function a level. The liquid where all. The Nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell. Xylem present in the vascular plants is made of cells that provide structural.
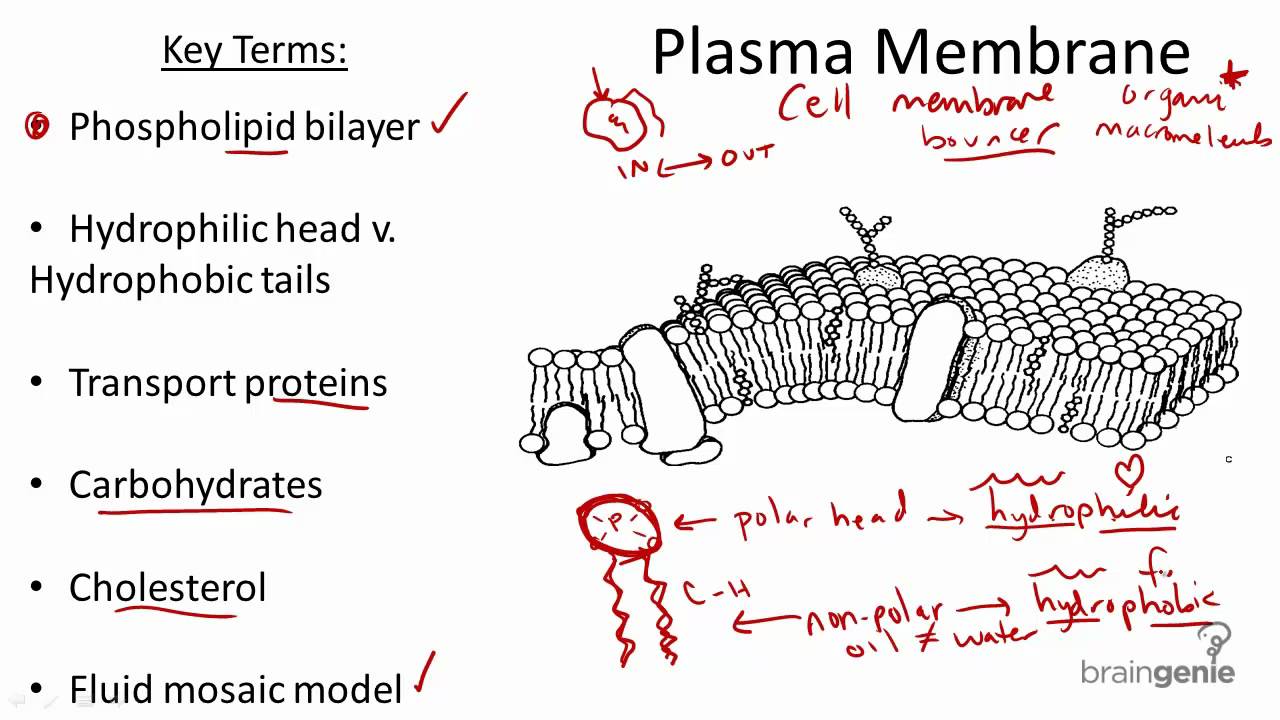
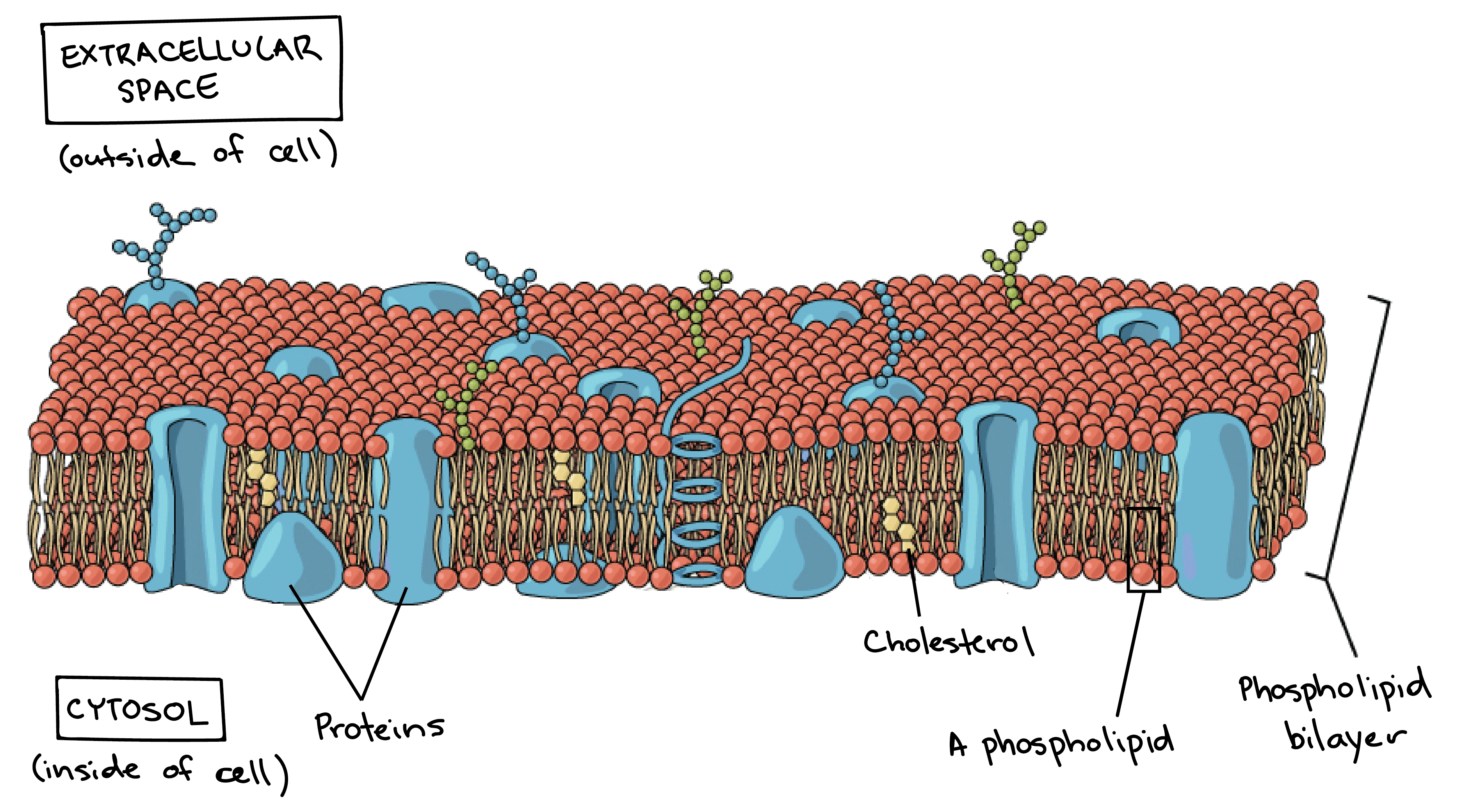
Membranes are selectively permeable so are effective barriers in controlling what goes in and out of cells. All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic ModelAccording to this model which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s plasma membranes are composed of lipids proteins and carbohydrates that are arranged in a mosaic-like manner. The cell wall and the cell membrane are the main components that function to provide support and structure to the organism.
Membrane Structure and Function All cells have a plasma or cell membrane which contains the cell. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cells cytoplasm.
Many membranes within the cell help to make different compartments for different chemical reactions to take place. The fine detail of the cell which may be revealed by an electron microscope is called the cells ultrastructure. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane.
Some of these proteins span the whole width of the membrane. -A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell. This is a thin flexible layer round the outside of all cells made of phospholipids and proteins.
Cell Membranes a outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells b state that plasma cell surface membranes are partially permeable barriers Plasma membranes are partially permeable meaning they let some molecules through but not others. Thin barrier separating inside of cell cytoplasm from outside environment Function. Formed from a phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each.