Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Hydrolysis Breaking a bond in a molecule and splitting it into smaller molecules through a reaction with water.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. During cellular respiration glucose in the presence of oxygen is converted into carbon dioxide and water. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration involve chemical reactions which take place in the cell to produce energy which is needed for active processes.
The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. The cellular context In the diagram at left 1 represents the cell exterior. But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP.
Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water.
Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule.
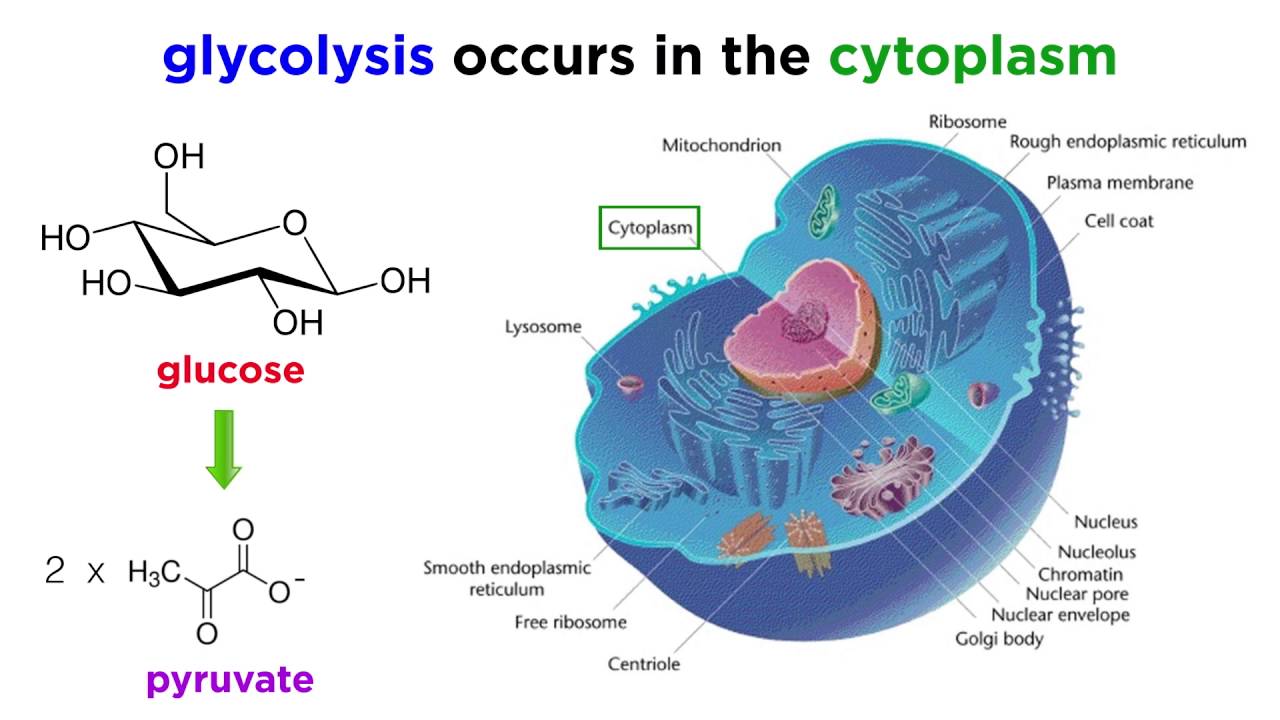
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration.