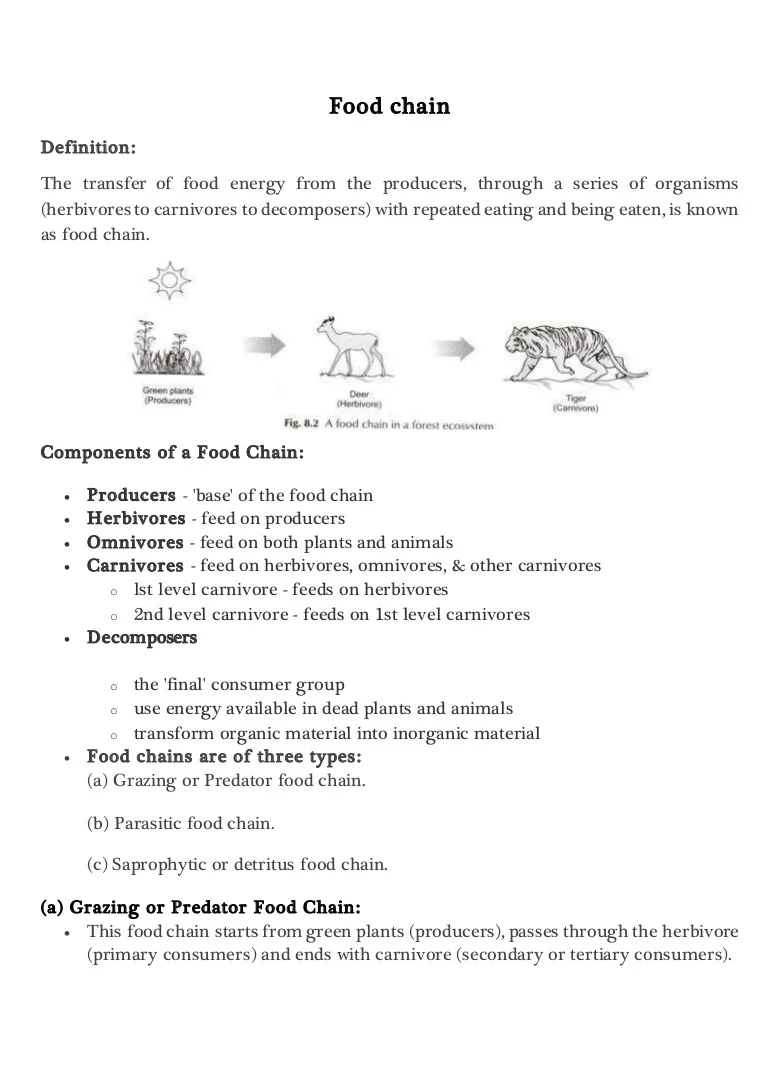
Food Chain Definition Ecology

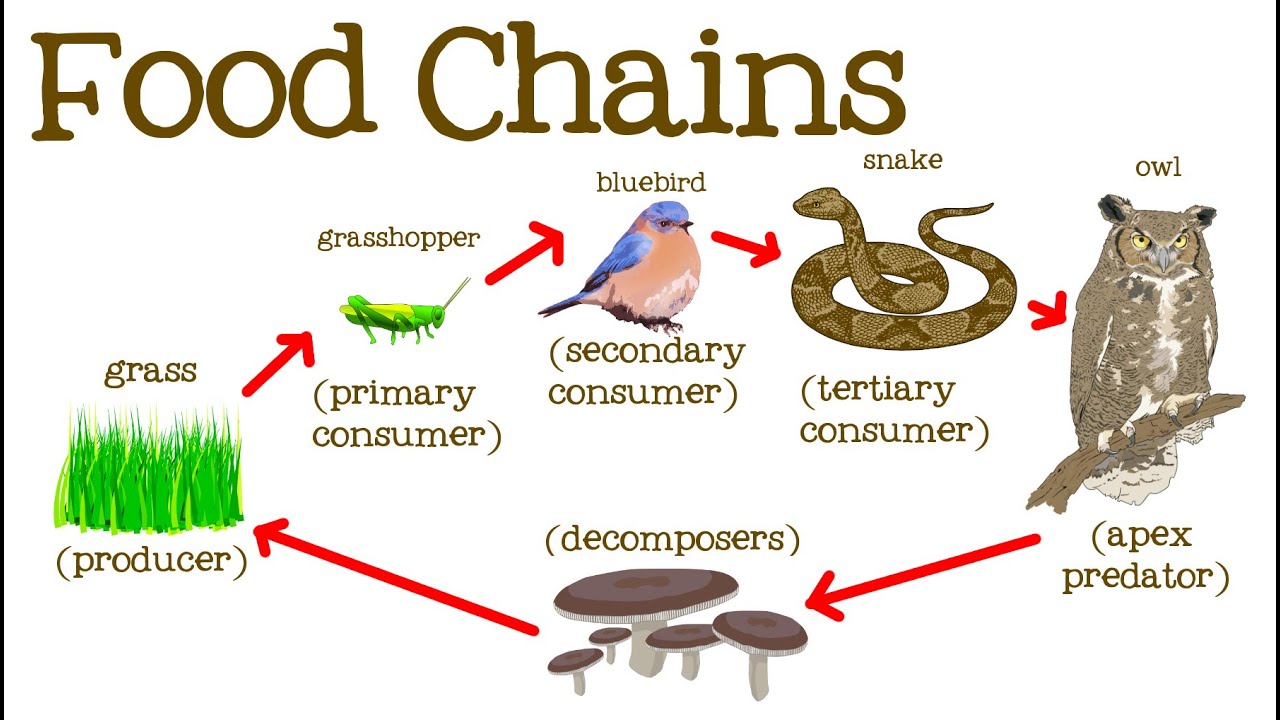
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants grasshoppers frogs snakes and hawks figure 83.
Food chain definition ecology. The sequence of organism through which the energy flows is known as food chain. Carl Linnaeus in an ecologically important essay The Economy of Nature Linnaeus Latin 1749. Forest ecosystem food chain Google Search Forest meaning pronunciation translations and examples.
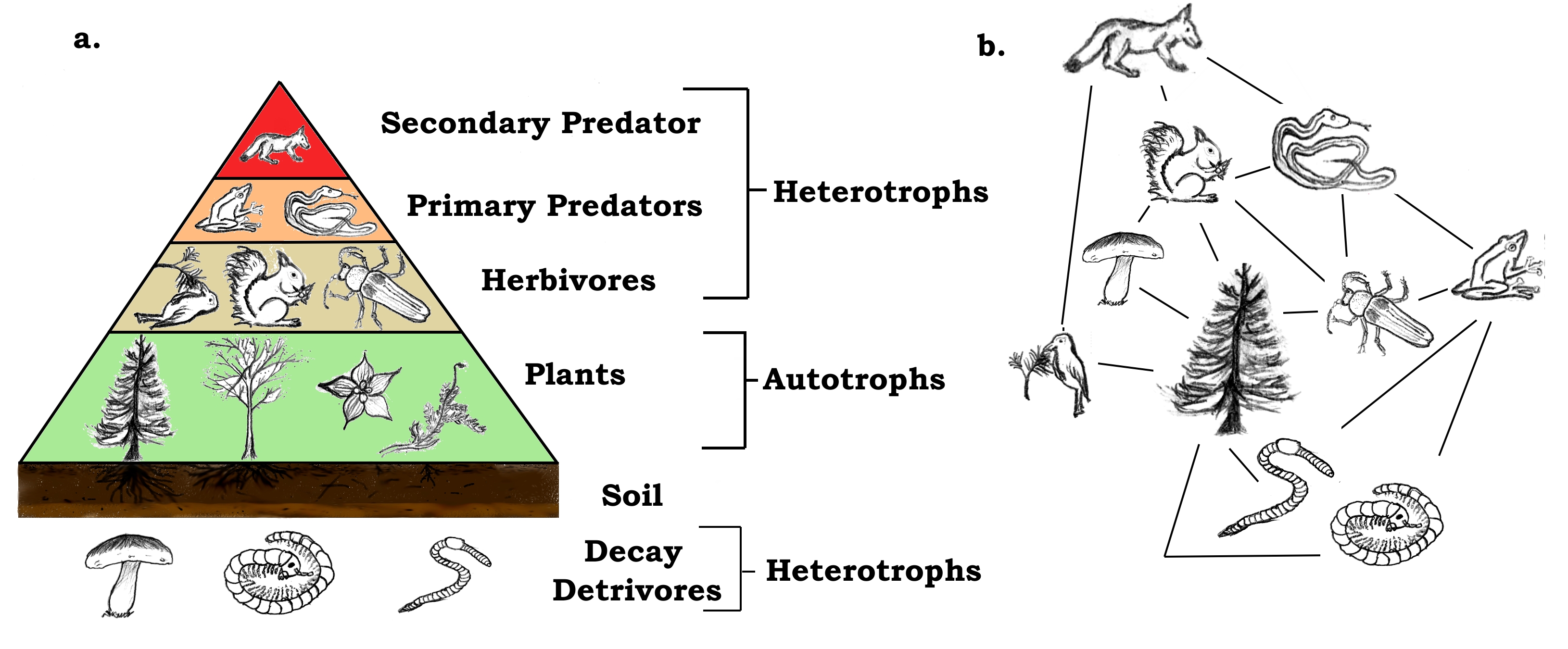
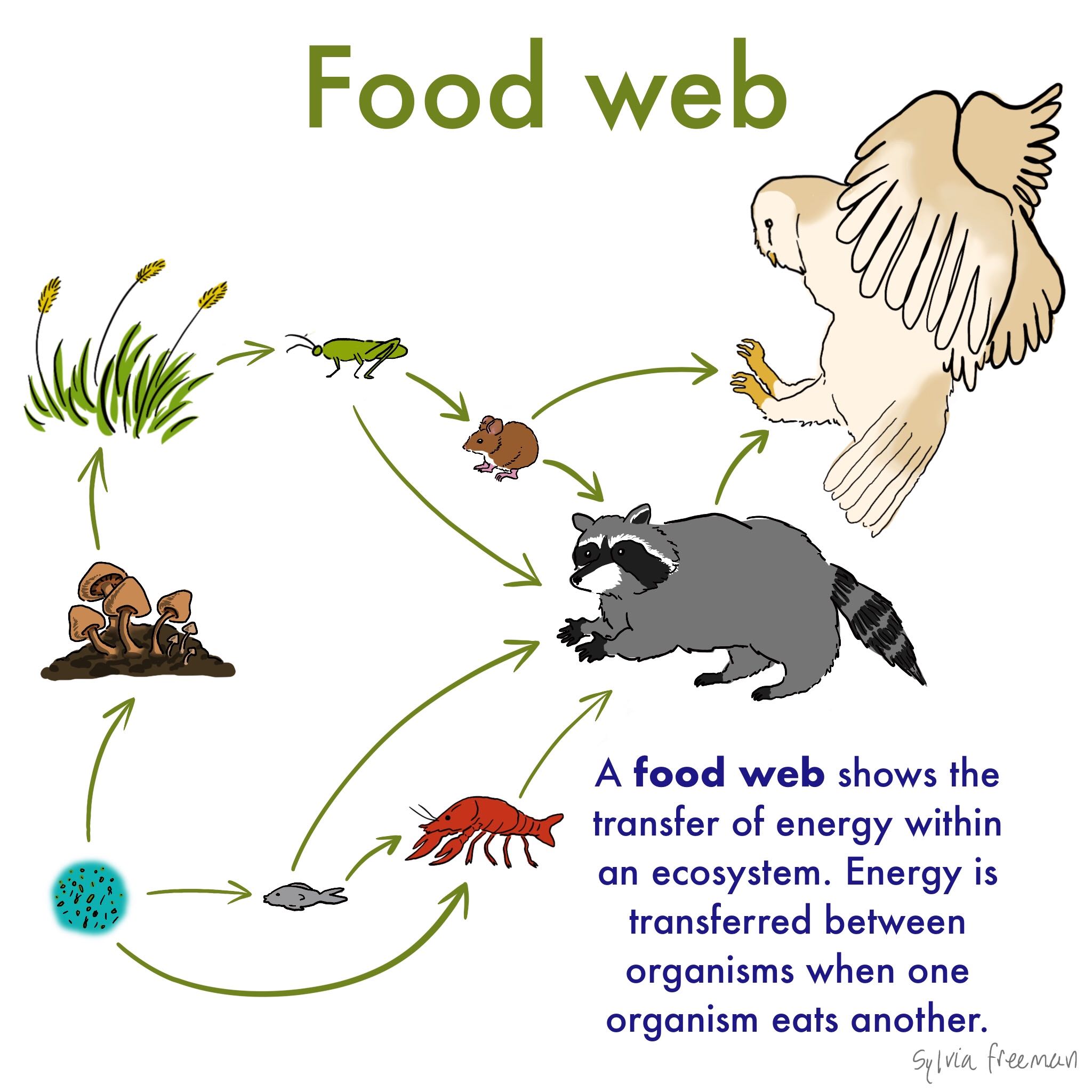
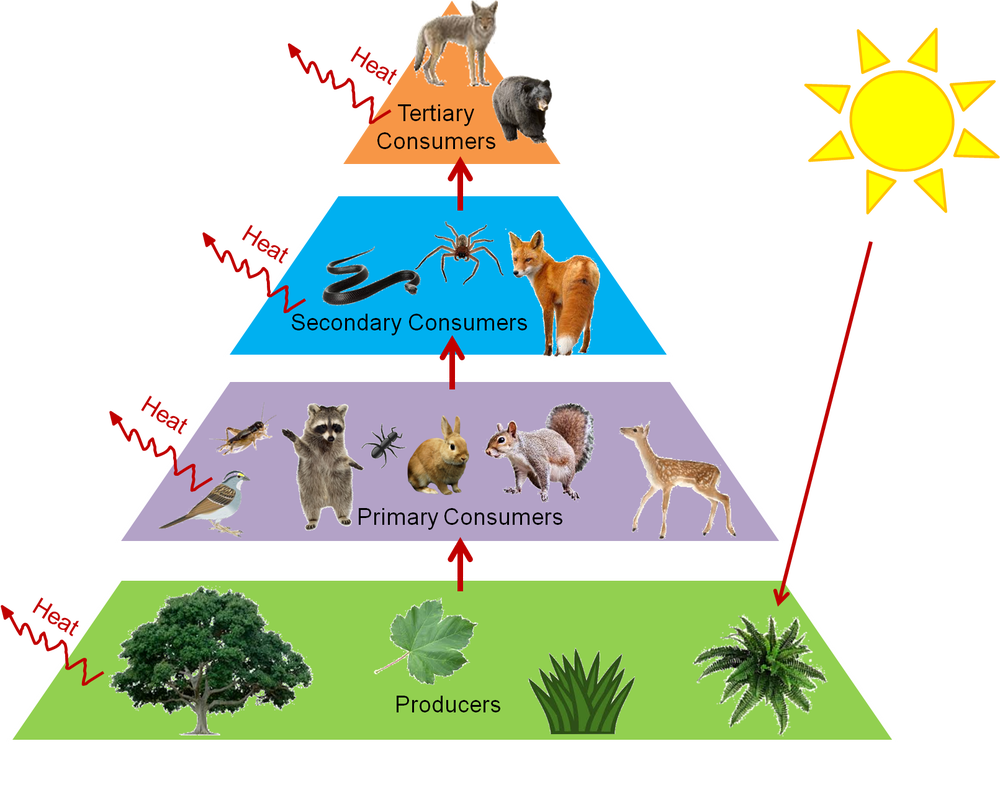
The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy are transferred from one organism to another. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaa food chain also shows how the organisms.
Video about Food Chain Definition Ecology. In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other. Each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrient s can follow through the ecosystem.
In ecology a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. In 1927 he recognized that the length of these food chains was. That is they can form one of the links in a food chain.
There are likely other naturalists between Linnaeus and Darwin who reported on food chains but attracted little notice. Plants are eaten by insects insects are eaten by frogs the frogs are eaten by fish and fishes are eaten by humans. The term food chain describes the order in which organisms or living things depend on each other for food.
The producers are represented primarily by the green plants and to a lesser extent by the photosynthetic bacteria. The sequence of the transfer of food energy from one organism to another in an ecological community. Weve got you covered.